Introduction
Lean is a systematic approach to maximizing value while minimizing waste in any process. It originated from the Toyota Production System (TPS). Lean principles help businesses improve efficiency, reduce costs, and enhance customer satisfaction.
The methodology is a proven approach to delivering greater value to customers., it has been since adopted across industries—from manufacturing to healthcare and software development.
The 5 Key Principles of Lean (Core Principles of Lean)
The application of these principles in organisations generally streamline operations, boost productivity, and deliver higher-quality products and services. Let’s dive into the principles and Improvement cycle
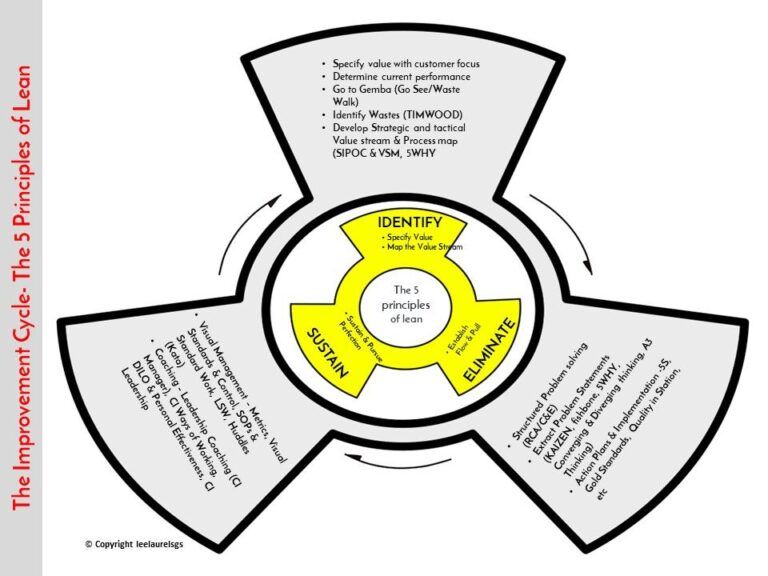
PRINCIPLES OF LEAN: Identify, Eliminate, Sustain
Identify
Define or Specify Value
Value is defined by the customer—what is the customer willing to pay for. For us at Leelaurels, it’s essential and critical to understand a clear definition of the needs of the customer (Anything that doesn’t contribute to this is waste) in other to eliminate unnecessary processes that don’t contribute to value. – Example: A software company discovers that users only care about fast load times and ease of use—extra features they don’t use are non-value-adding.
Key Questions:
Identify & Map the Value Stream
The next step for us will be to visualise inefficiencies in the process (Value Stream) by identifying every step in your process, from raw materials to delivery, and categorize them as:
The tool used to achieve this, is Value Stream Mapping (VSM). The Value Stream includes all steps (both value-adding and non-value-adding) required to deliver a product or service.
Waste Identification
Use tools like the 8 Wastes of Lean to pinpoint inefficiencies during Gemba walk/Go See
A core principle of Lean is eliminating waste—any activity that consumes resources without adding value. Toyota identified eight types of waste (often remembered by the acronym DOWNTIME):
Eliminate
Create Flow
Ensure a smooth, uninterrupted workflow by:
Establish Pull
Produce only when there’s demand to avoid overproduction (a major waste).
Root Cause Analysis: Use tools like the 5 Whys and Fishbone Diagram to address the source of problems.
Just-in-Time (JIT): Produce only what is needed, when it is needed, to reduce overproduction and inventory waste.
Standardized Work: Create consistent processes to minimize variability and errors.
Sustain
How to …:
Visual Management: Use tools like Kanban boards and Andon systems to maintain transparency and accountability.
Continuous Training: Equip employees with the skills and knowledge to uphold Lean practices.
Regular Audits: Conduct periodic reviews to ensure processes remain efficient and aligned with goals.
Pursue Perfection:
Lean is a continuous journey. Encourage a culture of Kaizen (continuous improvement) through:
Example: An assembly line rearranges workstations to minimize movement, speeding up production.
Cutting waste leads to faster delivery, lower costs, and higher quality.
By focusing on value and streamlining the value stream, businesses reduce waste and improve efficiency.
Conclusion
By applying these five Lean principles, businesses can reduce waste, improve efficiency, and enhance customer satisfaction.
Call to Action: Ready to transform your organization? Begin with a Kaizen Walkthrough today, embrace Lean principles, and build a Culture of Improvement that drives lasting success!.
Need help implementing Lean? Contact/Get in Touch with our Certified Lean practitioners. (info@leelaurelgs.com, +2348062905881, +234817409633)
Contact Us
leelaurelsGS
Tel +234 8177409633, +2348062905881,
email – info@leelaurelsgs.com
website – leelaurelsgs.com
