We have explored the principles of Lean methodology—covering its principles, culture of continuous improvement, value stream mapping, waste elimination, and sustainability. Now, it’s time to tie it all together and show how Lean transforms processes and operations.
RECAP – Lean Principles
Before diving into case studies, let’s revisit the five core Lean principles: and tie it all together
In operational terms:
2. How All Lean Elements Work Together
Lean Component | Operational Application | Impact |
Specify Value | Identify the Customer Value & Focus on production uptime, not just activity | Aligns teams on true business priorities |
Value Stream Mapping | Identify bottlenecks in production, logistics, etc | Exposes hidden inefficiencies |
Flow & Pull Systems | JIT inventory for spare parts | Reduces capital tied up in warehouses |
Continuous Improvement (Kaizen) | Deploy daily Cadence/Kata & Focusing on Daily operational problem-solving huddles | Creates a culture of innovation |
Kaizen Walkthrough
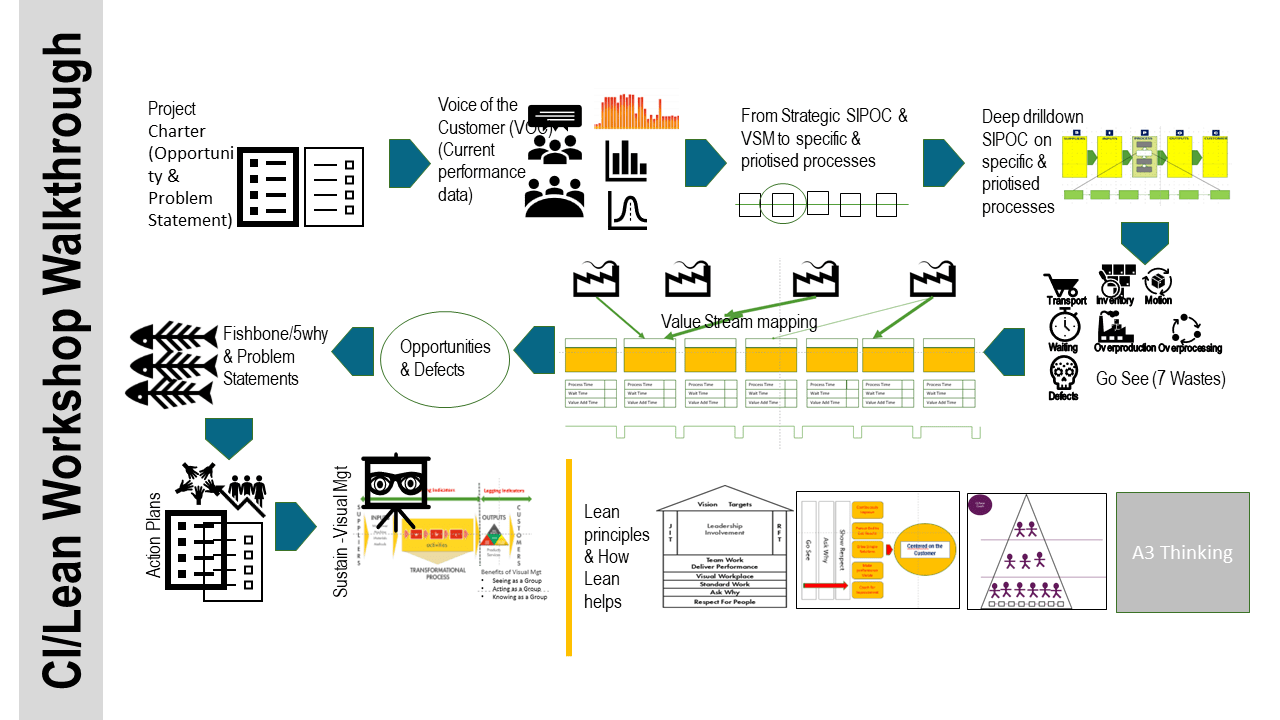
Sustaining Lean: Making It Stick
Many companies start Lean but fail to sustain it. Here’s how successful oil & gas firms maintain momentum:
Leadership Commitment
Employee Engagement
Standardization
Continuously Improve
Visual Management
Digital Lean Tools
These pillars work together to create a culture of excellence and adaptability.
They show how Lean principles apply consistently across industries when you:
Key Lessons and Tools
Conclusion: Lean as a Competitive Advantage
Lean isn’t just a cost-cutting exercise—it’s a culture of continuous improvement that:
✅ Boosts profitability
✅ Enhances safety
✅ Future-proofs operations
Your Next Steps:
Need help implementing Lean? Contact/Get in Touch with our Certified Lean practitioners. (info@leelaurelgs.com, +2348062905881, +234817409633)
Contact Us
leelaurelsGS
Tel +234 8177409633, +2348062905881,
email – info@leelaurelsgs.com
website – leelaurelsgs.com
